AJRCCM:A Large-Scale Exome-Wide Association Study Identifies
Novel Germline Mutations in Lung Cancer
On 11thMay2023, researchgroup of Professor Feng Chen, School of Public Health, NanjingMedicalUniversitypublished a research article entitled "A Large- Scale Exome-Wide Association Study Identifies Novel Germline Mutations inLung Cancer".

Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths and a critical barrier to increasing life expectancy worldwide. Previous studies have identified several rare germline mutations associated with the risk of lung cancer, including those in BRCA2, CHEK2, and ATM. However, most of these are based on single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays, which have a limited scope and accuracy for genetic variant detection. The UK Biobank (UKB) provides detailed cancer follow-up information linked to whole-exome sequencing (WES) for approximately 450,000 participants, offering an unprecedented opportunity to evaluate the effects of germline mutations.
In this study, the UK Biobank Exome Sequencing Project was uesed as the discovery set and the PLCO, ILCCO-OncoArray, TRICL, and FinnGen SNP array-based projects were used as replication sets, and a total of 683,214 populations were enrolled to analyse the genetic variations in the human exome and lung cancer susceptibility.
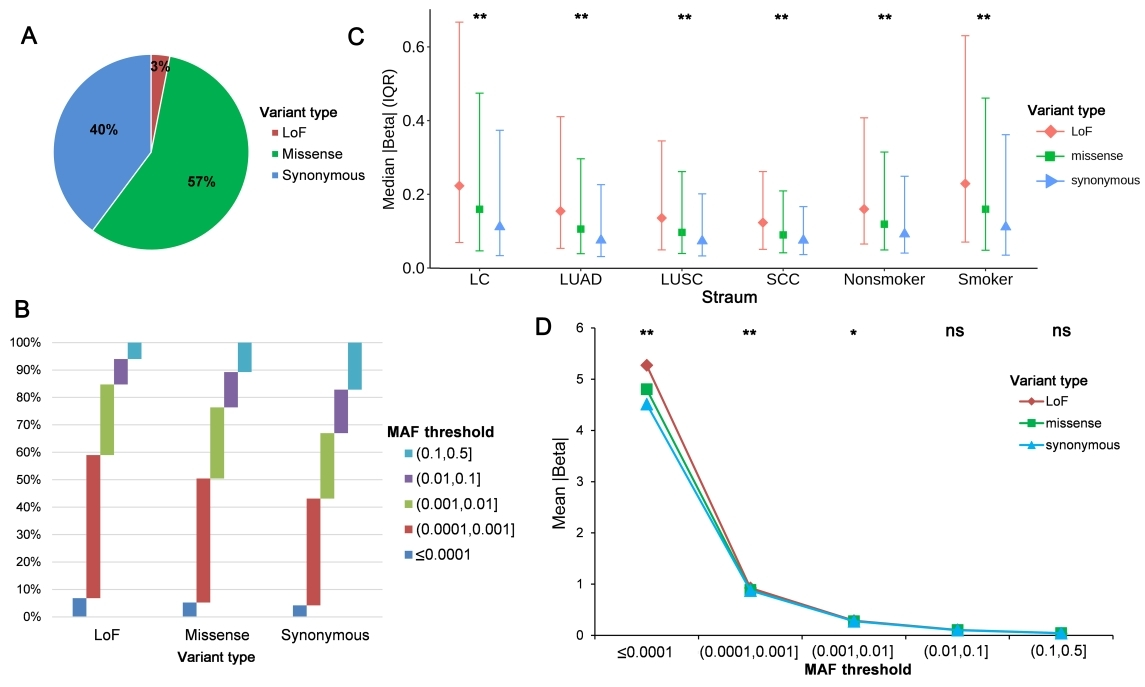
The study analyzed the effects of LoF, missense, and synonymous variants on predisposition to lung cancer. LoF variants tended to have lower allele frequencies and larger effects in overall lung cancer or lung cancer subgroups, whereas missense variants had moderate effects. The effect differences disappeared when the MAF increased (>0.01) for all three variant types.
The article systematically analyzed 216,739 SNVs in the human exomes by quality control,resulting in the identification of eight representative SNVs in the total lung cancer population or smokers that reached genome-wide significance levels(5×10-8) of representative SNVs, including two newly identified missense mutations TET3(2p13.1), POT1(7q31.33), two newly identified synonymous mutations TMEM173(15q25.1), ATRN(20p13), and remaining four mutations: TERT(5p15.33), MHC(6p21.33), CHRNA5(15q25.1), and CYP2A6(19q13.2), which were consistent with those found in previous GWAS studies.

The study also analysed the association of eight SNVs identified with potential intermediate exposure to lung cancer, including lung cancer-related chronic diseases and well-known risk factors for lung cancer. Significant exposures for each germline variant were identified, some of which showed strong relationships with multiple exposures, such as CHRNA5, MHC, and CYP2A6.
This study provides novel insights into human exomes and germline mutations through comprehensive analyses of the genetic predisposition to lung cancer and subsequent target analyses of specific exposures and genes. Associate Professor Sipeng Shen, Department of Biostatistics, School of Public Health is the independent first author of this article.
Time:May,2023
Journal:American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
Title:A Large-Scale Exome-Wide Association Study Identifies Novel Germline Mutations in Lung Cancer
Link:https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202212-2199OC

